iOS Views
In this section we discuss about the various UI controls used to build iOS user interfaces. Let's start about discussing about storyboards.
Storyboard
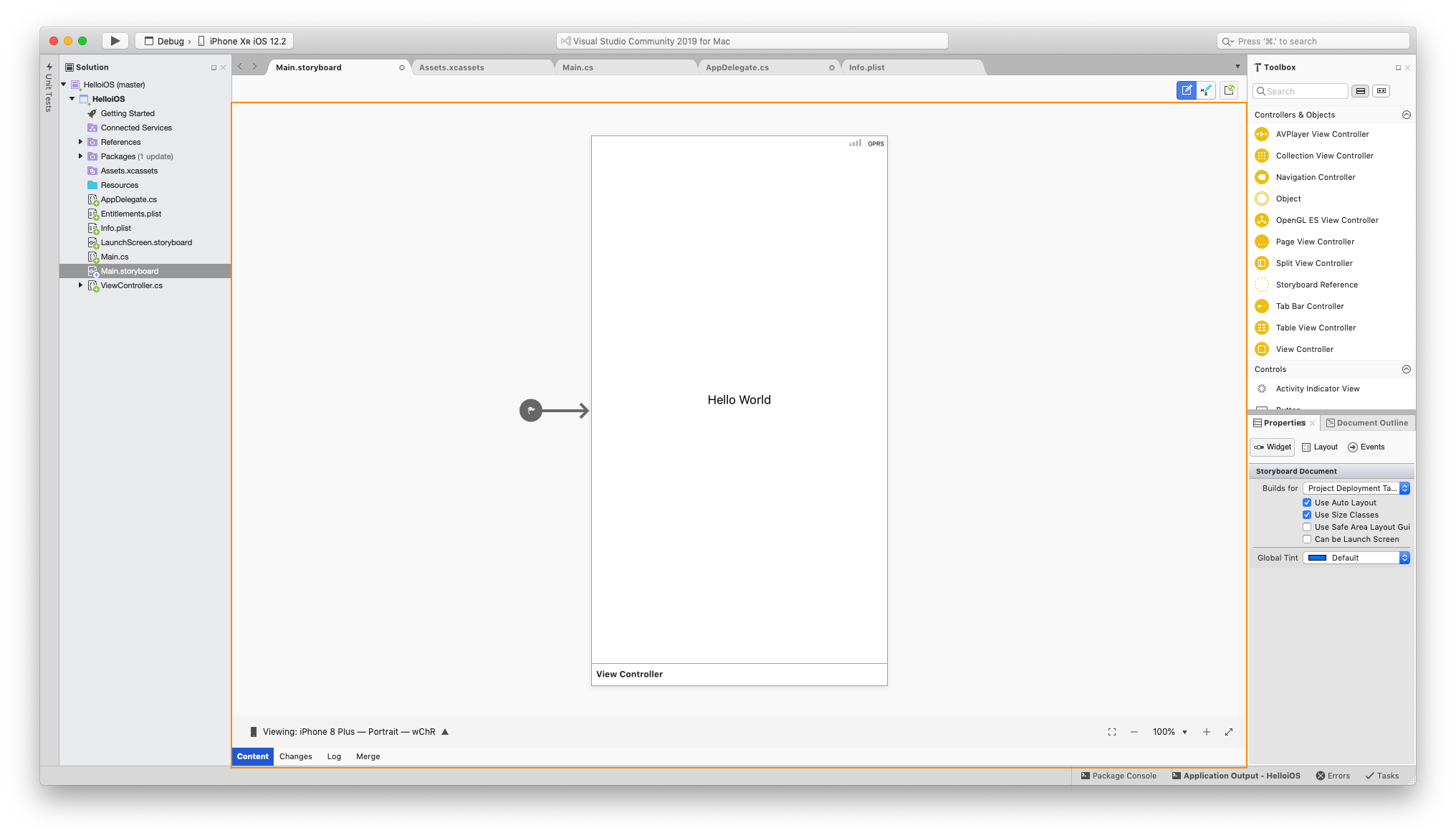
A Storyboard is a file that contains the visual designs of our application’s screens as well as the transitions and relationships between the screens. The storyboard files end in the .storyboard extensions.
What is the difference between xib and storyboard files?
In the beginning, to design iOS screens, you had to create one file for each screen. These files were called xib files. In later versions of iOS you could design multiple screens in one place, this file is called the storyboard.
Scence
The combination of a ViewController and its views is called a Scene in the storyboard. You will have multiple Scenes for each of the screens for your app. When a new Single View Application project is created from a template, Visual Studio for Mac automatically generates a Storyboard file called Main.storyboard and populates it with a single Scene.
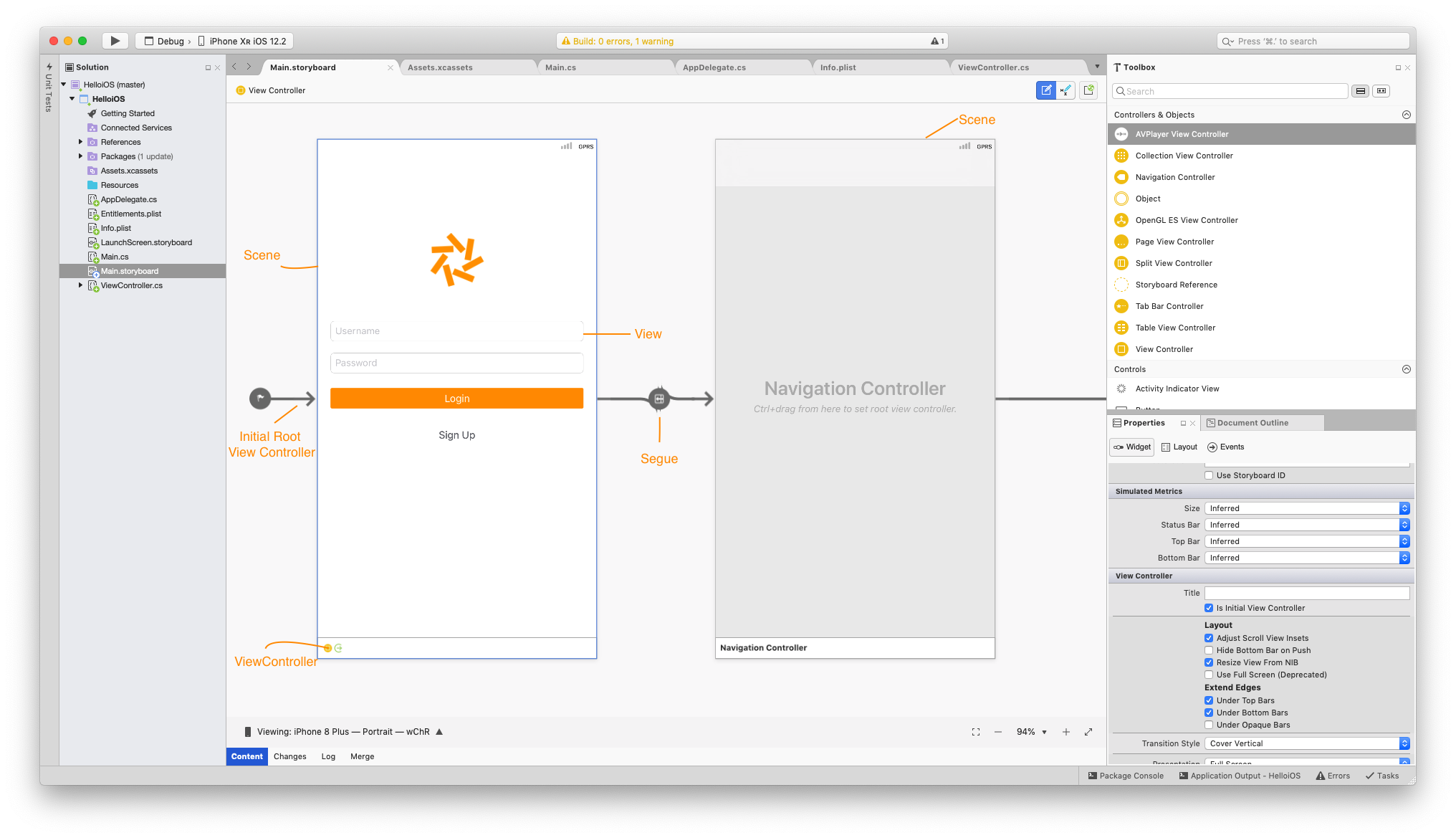
ViewController
The view controller is an instance of the UIViewController class that contains the backing code. You wire the event and all the logic in the viewcontroller.
MVC
iOS uses the MVC design pattern. The ViewController combines the View and Controller into one object called the ViewController.
View
Each ViewController have a view it controls. The View is an instance of the UIView class that defines an area of the screen and provides interfaces for working with the content in that area. The default View is a single Root View that fills the whole device screen.
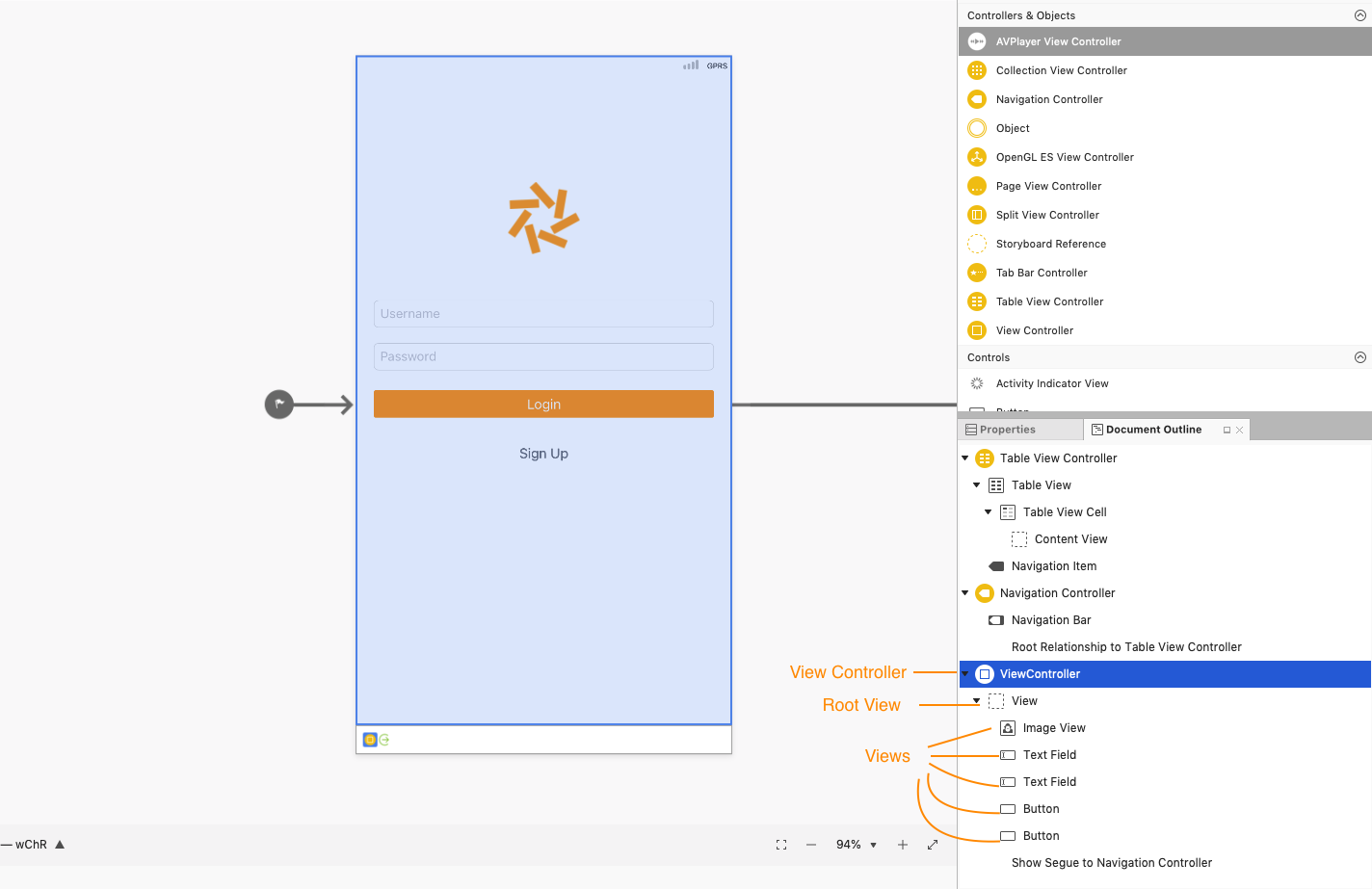
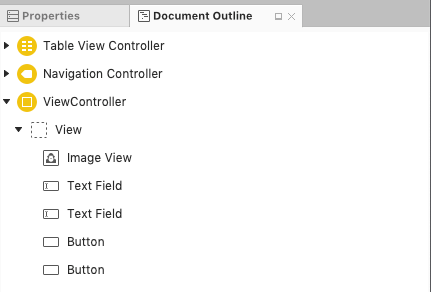
The outline of all the elements in the scene can be viewed by examining it in the Document Outline pad:
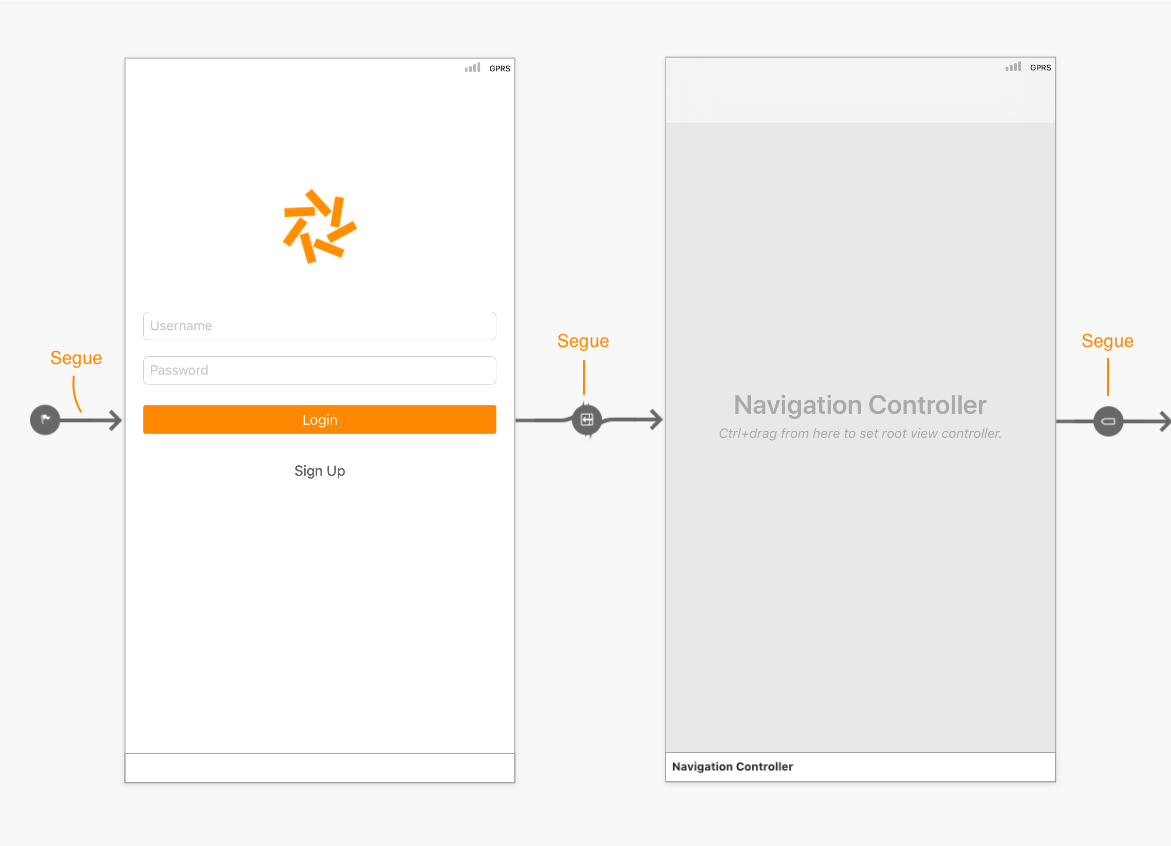
Segue
A segue(pronounced seg-way) is the transition from one scene to the next. Its represented with an arrow on the storyboard. They are different types of segues and we will discuss them in later chapters.
Window
The AppDelegate class manages the application Window. The Window is a single instance of the UIWindow class that serves as a container for the user interface.
By default, an application gets only one Window onto which to load its content, and the Window is attached to a Screen (single UIScreen instance) that provides the bounding rectangle matching the dimensions of the physical device screen.
The figure below shows the relationships between the different components:
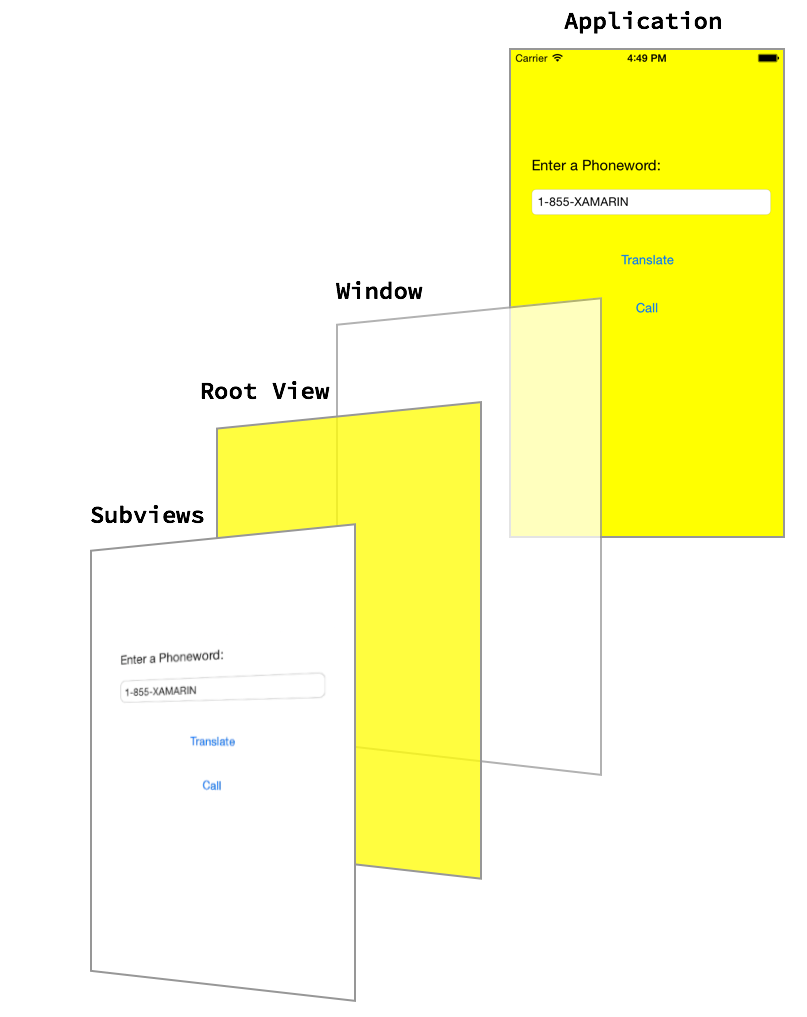
These additional Views are inside the Root View are called Subviews.
Common Views
Let's now look at the different sub views we use to create the UI. We are going to look at the following views:
- Label
- TextField
- TextView
- Button
- Slider
- ImageView
- ActionSheet
- Segmented Button
- Switch
- Stepper
- Date Picker
- Alert View
- Web View